+95 9443223999 | info@biyedu.com
+95 9443223999 | info@biyedu.com
This study, conducted in 2019, covers the modern ‘Grab’ service in Yangon, Myanmar – Grab Taxi, Grab Bike, Grab Hitch and Grab Express services. The SERVQUAL model was chosen as the most suitable method for quantitative findings. A total of 100 questionnaires, with a Likert type scale, were distributed to a sample of 90 Grab customers ( riders), aged 18 or more. A descriptive survey design was used to collect data on service quality and customer satisfaction simultaneously. Data analysis was conducted by descriptive statistics and inferential statistics and narrations.
The study results indicated a good relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction. Out of the five dimensions of the SERVQUAL- Reliability, Responsiveness and Assurance had high significant impact on customer satisfaction, whereas Tangibles and Empathy had a low impact. The study concluded that service quality confirms its role as an important driver of customer satisfaction, which leads to customer loyalty and thereby, profits and success. These findings could be applicable and useful for various businesses and their managers and an invaluable insight for management strategies.
So, it is important for the service provider to give better customer service and more satisfaction to customers in order to increase revenue, profits and sustainability for the future.
Keywords: Service quality, Customer satisfaction, Grab Taxi, SERVQUAL model
This study stemmed from the researcher’s pure motivation, curiosity and interest. Its driving force was the new Grab taxi service running in Myanmar’s urban community. It is a fairly modern system with smart user services plus other striking new services like Grab Taxi, Grab Bike, Grab Hitch and Grab Express. There is little research on the taxi industry in Myanmar at large, and the concept of service quality and customer satisfaction for Grab taxi service has not been examined at all.
There are many challenges in today’s business world - globalisation, high competition, rapid changes in customer preference and taste, as well as technology and innovation. High quality vital. Firms need to understand a customer’s specific requirements, improve existing service features, and adopt new or unique ways of service delivery. Service quality is key. Many companies today are developing service quality in order to establish and maintain a loyal customer base.
Service quality can be defined as the degree to which customers' perceptions of service meets or exceeds their anticipation (Zeithaml, Berry & Parasuraman, 1990).
Customer surveys can measure the level of satisfaction and help in, understanding their expectations, finding out where the organisation is failing, pinpointing the specifics, assessing the competition and measuring emotional aspects as well as the customer loyalty. Customer satisfaction provides an indicator for the future. So, service providers need to know customer expectations and how to provide the best quality service to attract new customers and retain existing ones (Angelova & Zekiri, 2011). Firms need to deliver unrivalled quality services, create brand loyalty and strengthen their position in the industry.
Transport comprises buses, trains, taxis and other forms of transport. In general, taxis are a suitable choice for people living in or visiting the city, especially those who are unfamiliar with their destination. Convenience is one of the most important factors. Taxis have become the most popular and effective mode of transport for convenience, comfort and contentment.
At present, there are more than 800,000 registered vehicles and cars and taxis in Yangon comprise 70% of the total traffic (Htin, 2017). Taxis are easy to find everywhere in Yangon. The taxi firms fall into two broad categories, technology-based and traditional. Traditional taxi operators are individual taxi owners who park at strategic points to attract passengers, or respond to someone hailing a cab passing by on the road. In contrast, technology-based firms like Uber and Grab, use mobile apps or app-based ride-hailing, and are taking over traditional taxi service. People use smartphones as advanced, convenient, safe and effective communicative transportation tools, to bring taxis to them.
Grab ride hailing taxi service started in Myanmar on 21 st March 2017, and since then has attracted numerous customers and drivers. Uber had announced its arrival prior to Grab, but Grab caught Uber off-guard by launching a beta or trial version with a selected group of drivers. Grab was able to establish driver-partners relationships as soon as they entered (Grab Myanmar, 2019). Grab has been operating in three cities, Yangon, Mandalay and Bagan and offering Grab Taxi, Grab Share, Grab Thonebane and Grab Shuttle services.
There are local taxi services like Get Ride, Hello Cab, OK Taxi, Oway Ride and Kilo Taxi (Lee, 2017) and new businesses are entering the ride-hailing market. Competition is getting tougher, and Grab needs to provide quality services and a good brand image to maintain its market share and sustainable competitive advantage. Service quality is a fundamental strategy for high customer satisfaction, and thereby a positive image, performance and profitability.
This research aims to measure the impact of service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction and discover the impact of different variables specifically in the Grab taxi service in Myanmar. The specific objectives are defined by the research questions in 1.5.
These questions refer specifically to Grab taxi service.
(a) What is the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction?
(b) Which are the most and least influencing factors of customer satisfaction?
(c) What solutions should Grab Myanmar consider to improve customer satisfaction for long- term sustainability?
Descriptive research design was used to study issues and attitudes systematically and to enhance reliability, credibility and validity. This approach was apt as the study intended to gather data on the assessment of service quality and customer satisfaction.
This study could help top management and the marketing department of Grab Taxi in formulating suitable policies and strategies to gain and retain current customers, and thereby partially help the company to increase revenues, profits and sustainability advantages. The findings also may be beneficial to industry players who could benchmark with other companies as they formulate and adopt service quality to meet customer satisfaction. Furthermore, the study may also interest scholars as a basis for future research.
Customer satisfaction is defined by (Kotler & Keller, 2012) as “an individual’s feelings of pleasure or disappointment deriving from contrasting a product perceived performance with their expectations”. (Agbor, 2011) stated that customer satisfaction is affected by service quality in service industry. (Nguyen Hue Minh,et,.al, 2015) confirmed that service quality is a strong driver for customer satisfaction in hotel service in Vietnam. In addition, (Ramesh & Manju, 2017) found it is a critical prerequisite for establishing, maintaining, sustaining, enhancing and satisfying relationship with valued customers. Kotter & Keller (2012) said that due to those findings, in order to create customer relationship, firms must deliver superior and tailored products/ service compared to its competitors.
Service quality has a close relationship with customer satisfaction, particularly in-service industries, and is regarded as a major factor for success (Dachyar & Rusydina, 2015). Parasuranman (1988) identified service quality as the capacity of the company to conform with or outdo customer expectations, so, service quality may be seen as a comparison of expectations with perceptions, and sometimes there is a gap between these. (Azizi & Moghadam. 2014) suggest that understanding customer's expectations and perceptions can help managers in strategic planning, marketing and organisational development plans.
Amongst various models which describe service quality, the most well-known scale of measurement is SERVQUAL, developed by Parasuraman, Zeithaml & Berry (1985). This was designed to measure quality in the service sector. It originally measured ten aspects of service quality, but later the ten components were collapsed into five dimensions (RATER):
Reliability – ability to perform promised service dependably and accurately
Assurance – employees’ awareness and politeness and their confidence and competence
Tangibles – making physical factors appealing ; i.e. equipment, facilities, staff, premises
Empathy – caring attitude towards individuals
Responsiveness – willingness to help customers promptly and handle complaints
Reliability – proved to have a big impact on customer satisfaction (Balachandran & Hamzah, 2017; Horsu & Yeboah, 2015).
Assurance – creates credibility and trust (Ramesh & Manju 2017). Tessera, et al (2016) found it had the highest impact on customer satisfaction for Ethiopian customers in the hotel industry.
Tangibles – Dachyar & Rusydina (2015) found tangibles to affect company image and customer satisfaction.
Empathy – an essential element for customer satisfaction (Tessera, et al, 2016; Sharma, & Saptarshi, (2017; Nguyen & Anh, 2015).
Responsiveness – service providers need to be courteous in delivering services (Azizi & Moghadam, 2014). A study by Techarattanased, (2015), focusing on metered taxi services service quality in Bangkok, Thailand, found responsiveness was a significant factor in service quality and customer usage.
Many researchers have studied customer satisfaction in various countries. Dachyar & Rusydina (2015) measured customer satisfaction in the taxi service and service quality in Jakarta. Later Khuong & Dai (2016) looked at customer satisfaction and loyalty in taxi companies in Ho Ci Minh City, Vietnam, and Balachandrian & Hamzah (2017) researched the influence of customer satisfaction on ride-sharing services in Malaysia.
This paper uses SERVQUAL on RATER with some customisations. The aims are:
The analytical framework is proposed based on the related research studies and consists of the five main independent variables, RATER. The dependent variable is customer satisfaction.
These dimensions have been extensively accepted and applied by many academics and managers in various industries, and are applicable in taxi services.
Tangibles – appearance of physical facilities including car condition, GPS system, drivers’ appearance and visual materials.
Reliability – ability to perform the promised service dependably and accurately.
Responsiveness – willingness to help customers and provide prompt service.
Assurance – knowledge and courtesy of drivers/employees and their ability to inspire trust and confidence.
Empathy – Trustworthiness, believability, honesty, caring, individualised attention provided to customers.
The hypotheses have been developed from the research objectives and questions

Hypothesis 1: Tangibles have a positive impact on Customer Satisfaction.
Hypothesis 2: Reliability has a positive impact on Customer Satisfaction.
Hypothesis 3: Responsiveness has a positive impact on Customer Satisfaction.
Hypothesis 4: Assurance has a positive impact on Customer Satisfaction.
Hypothesis 5: Empathy has a positive impact on Customer Satisfaction.
Research methodology is used for collecting information and data for the purpose of making a business decision. The objectives of this research are:
(1) To find the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction
(2) To investigate the most and least influencing factors of customer satisfaction for Grab Taxi Service in Yangon.
Both primary and secondary data were collected. Questionnaires were sent to 100 respondents from Yangon City, all of whom were over 18 and had experience of using Grab Taxi Service. The questions included demographic details. A google form was provided to collect responses, confidentiality was assured. This method of collection is quick and inexpensive.
The questions were structured around the dependent variables (customer satisfaction) and the independent variable (service quality). Service quality was measured via the SERVQUAL model which incorporates five dimensions, namely, Tangibles, Reliability, Responsiveness, Assurance and Empathy. There were five items for each of these and five items for customer satisfaction. A 5-point Likert scale was used, a score of 1 denoting they strongly disagreed and a score of 5 that they strongly agreed. The analysis was carried out with SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Science) and the findings/data are placed in tables to summarise them.
3.1 Limitations and Constraints in the Research Time constraints and lack of financial resources prompted the researcher to focus the study on the Yangon area only. Moreover, the researcher has to base the findings on customer’s side, due to lack of information concerning Grab Myanmar. The sample size is expected to be around 100 respondents, however, there were some unpredicted errors in the outcomes which resulted in some changes in respondent numbers due to time limitation and human error.
Most of the respondents were female, aged between 18-30 years.
Marital status: 62% married, 38% single.
Income: 22% 300,000--600,000 kyats per month
Income: 20% 600,000--900,000 kyats per month
Income: 52% over 1,000,000 kyats per month
To examine the data reliability of the scale dimensions, Cronbach’s Alpha coefficient analysis was used. The reliability statistics was displayed in Table 1.

Table 1 shows the reliability coefficient of Cronbach's Alpha of all factors is ranged between 0.7 and 0.9. This proves a good strength of association of the factors. A reliability coefficient of 0.7 or above shows high internal consistency Customer satisfaction levels on service quality dimensions were analysed.
Figure 2 shows that the highest customer satisfaction levels came from Reliability, closely followed by Responsiveness, with Assurance not far behind. Tangibles lagged behind, and Empathy is the factor which Grab most needs to improve.
Tables 2 and 3 represented association between service quality and customer satisfaction. The service quality variables were tangible, reliability, assurance, responsiveness and empathy while dependent variable was customer satisfaction.


According to Table 2, R = 0.534, which indicates a moderate relationship between customer satisfaction on the service quality dimensions of Reliability, Assurance, Tangibles, Empathy and Responsiveness. The R Square was 0.285, which means that about 29 % of variations in the customer satisfaction could be attributed to factors outside the scope of this research. Table 3 shows that the F test statistics and significance value are 6.704 and 0.000 respectively, which means the model specification is fit for the study.

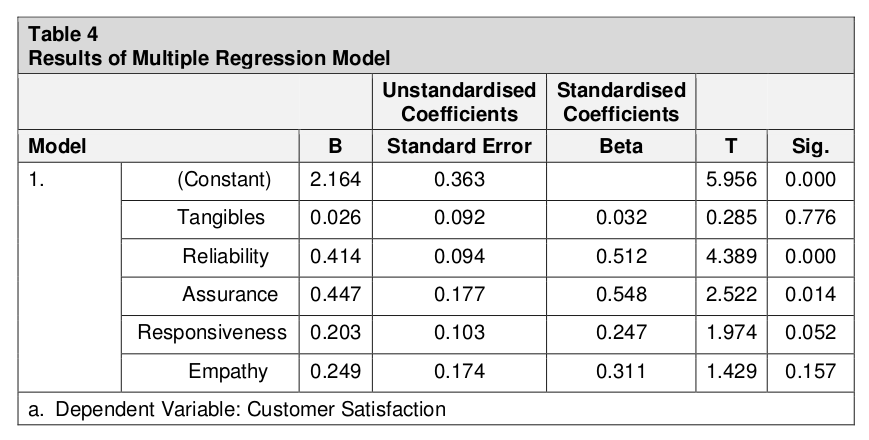
The coefficients of service quality dimensions show a positive impact on Reliability, Responsiveness and Assurance, and a negative impact on Tangibles and Empathy.
Tangibles – T value 0.285, which is greater than 0.05 (5% level of significance) so tangibles did not show a positive impact. This is contrary to results found by Bhatt & Bhannawat, 2016) and (Balachandran & Hamzah, 2017), who found a positive and significant relationship. However, customers mostly focus on responsiveness and time reliability as car condition is not their prime objective for travelling.
Reliability – T value 4.389, significance value of 0.0. This shows a positive and significant impact on customer satisfaction. Customers may feel satisfied as taxis are available 24/7 and taxis arrive on time. Commuters are reported to say timely arrivals and notification of any delays improve their satisfaction.
Responsiveness – positive regression coefficient 0.247. Responsiveness is defined as the willingness to help customers and several researchers include prompt service. This result is in agreement with the general consensus.
Assurance – also statistically significant, showing a strong correlation between Assurance and customer satisfaction.
Empathy – Table 4 shows that the t test statistics and significance value of “Empathy” are 1.429 and 0.157. Its significant level of the significance value is greater than 0.05 (5% level of significance) as well. So, “Empathy” has no positive impact on customer satisfaction.
In the case of Reliability, Responsiveness and Assurance, the regression result between the five independent variables and customer satisfaction have a significance value of less than 5 and T test statistics is more than 1.9, which are the required levels of significance for a positive result. So, in those cases the hypotheses were supported. This was not so for Tangibles or Empathy, so for those two variables the hypothesis was not supported. (See Table 5).


Based on table 6, satisfaction levels, in order of success, were as follows:
Reliability – 81.1%
Responsiveness – 78.9%
Assurance – 72.2%
Tangibles – 51.1%
Empathy – 47.8 %
This research adapted the SERVQUAL model to assess the impact of service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction towards Grab taxi service in Myanmar. Three research objectives were formed, concerning the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction, the most and least influencing factors on it, and possible solutions for Grab Myanmar for long-term sustainability in the highly competitive market.
The results show that service quality does impact customer satisfaction. Table 4 shows, through correlation and regression analyses that the impact is high for Reliability, Responsiveness and Assurance, but low for Tangibles and Empathy. All five factors had reached an agreeable level.
Reliability being the most influential factor, it is vital to perform the service dependably and accurately. Responsiveness and Assurance are also important, so the service needs to be warm, straightforward and transparent, and passengers need to feel safe. All of these will maintain the brand image.
As for any businesses, Grab Myanmar’s marketing and operations managers should regularly revisit their goals and objectives, evaluate and upgrade to improve their service offerings. Flexibility with reliability and consistent top-notch quality in responding to customers’ needs will give Grab Myanmar the positive edge and success in taxi business world. To achieve competitive advantage, the company should analyse the extent to which customers view alternative taxi service providers and their marketing attempts. Then, it should provide diverse categories of benefits and incentives in terms of price discounts, rewards, promotional programmes, social welfare and membership benefits. Finally, the company needs to pay attention to quality of the overall services and specific customer-oriented services to enhance customer satisfaction, as this is the strongest determinator of customer loyalty.
Paragraph 1.5 gives the research questions, which define the research objectives. These were completed by evaluating existing literature and distributing 100 questionnaires, the results of which were analysed using SPSS software. The independent variables (service quality dimensions) and dependent variable (Customer satisfaction) were determined through regression coefficients, t-value and significance value in order to meet the objectives and test the hypotheses.
This research analysed customer satisfaction through service quality, specifically in the areas of Tangibles Reliability, Responsiveness, Assurance and Empathy. Three of these, Reliability, Responsiveness, and Assurance showed statistically significant impacts on customer satisfaction. Reliability had the strongest impact with the highest beta coefficient value, followed by Responsiveness, and Assurance, Tangibles. Empathy had the least impact.
These findings can help Grab Myanmar to know which dimensions are the most important factors for customer satisfaction, which is useful information for improving service, attracting new customers, and turning these into loyal customers. The result confirms that service quality is an important driver of customer satisfaction which leads to customer loyalty and thereby profit and success. Therefore, service quality should be taken into high consideration in both academic and practical practices.
The researcher made some effort to fill the knowledge gap through data collection and analysis via respondents, but there is room for further research.
Firstly, two of the hypotheses were not supported (concerning Tangibles and Empathy). These could be tested in future studies with a larger sample size.
Secondly, this study mainly focused on the quantitative methods. Qualitative data could refine the findings and results.
Thirdly, the study was only about Grab taxi services in Yangon City. Future researchers could collect data from other cities where Grab operates, as well as comparing Grab with other taxi providers.
Fourthly, the study was limited to one industry. Similar investigations could be applied to other closely related industries for extensive research to get clearer view of what the service quality impact would be.
The findings of the study provide both academic and managerial implications. Using the SERVQUAL dimension to examine the relationship between customer satisfaction and service quality will help management to better understand what these dimensions mean to the customers, and how better to deal with customers effectively, to minimise cost and maximise profit, and to guide strategic planning.
This research paper can be used as a reference for other research papers from both same or different industries. It could also be used as a guideline for industrial analysis model and for business plans.
Agbor, J M, (2011) The Relationship between Customer Satisfaction and Service Quality: a Study of Three Service Sectors in Umea”. Umea School of Business
Angelova, B & Zekiri, J, (2011) Measuring Customer Satisfaction with Service Quality Using. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences , 1 (3)
Azizi, E, Jafari, D, & Moghadam, B F, (2014) Customer Expectations and Perceptions of ETKA Organisation's Service Quality Using SERVQUAL Approach (Case Study:
Pamizfam Sugar Company, Journal of Social Issues & Humanities, 2 2 (3), 90-92. Balachandran & Hamzah (2017) The Influence Of Customer Satisfaction On Ride-Sharing Services In Malaysia. International Journal of Accounting & Business Management , 5 (2), 186
Bhatt, A K, & Bhanawat, D S, (2016) Measuring Customer Satisfaction Using ServQual Model - An Empirical Study. International Journal of Trend in Research and Development, Vol 3 (1) Accessed from:
http://www.ijtrd.com/papers/IJTRD2425.pdf
Dachyar & Rusydina. (2015) Measuring Customer Satisfaction and its Relationship towards Taxi Service Quality around Capital City Jakarta. International Journal of Engineering & Technology , 15 (1), 27
Grab, (2019) Grab Myanmar
Accessed February 2 nd 2019 from:
https://www.grab.com/mm/en/about/
Horsu & Yeboah (2015) Influence Of Service Quality On Customer Satisfaction: A Study Of Minicab Taxi Services In Cape Coast, Ghana. International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management , 3 (5)
Htin, K, (2017) Yangon Government to Monitor Public Transport Using GPS. Eleven Myanmar , 4 (39), 12
Khuong, M N, & Dai, N Q, (2016) The Factors Affecting Customer Satisfaction and Customer Loyalty - A Study of Local Taxi Companies in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam; International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology, Vol 7, No. 5, October 2016 Accessed from:
http://www.ijimt.org/vol7/678-MB00013.pdf
Kotler, P, & Keller, K, (2012) Marketing Management, 14th ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall Lee, S, (2017) Ride-Hailing Market Heats up in Yangon. Frontier Myanmar , 13 (5), 8-9
Nguyen,M & Anh, P C, (2015) Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction: A Case Study of Hotel Industry in Vietnam, Asian Social Science, March 2015 , 11 (10), 73-84 Accessed from:
file:///C:/Users/CAROLI~1/AppData/Local/Temp/Service_Quality_and_Customer_Satis faction_A_Case_S.pdf
Parasuraman, A, Zeithaml, V, & Berry, L, (1985) A Conceptual Model of Service Quality and its Implications for Future Research. Journal of Marketing (Fall), 41-50
Parasuraman, A P, & Berry, L, (1988) SERVQUAL: A Multiple-Item Scale for Measuring Consumer Perceptions of Service Quality, Journal of Retailing, January 1988, 12 (1), 12-40
Ramesh, N, & Manju D, (2017) Evaluation of the Impacts of Service Quality Dimensions on Patient/Customer Satisfaction: A Study of Private Hospitals in Nepal. International Journal Social Sciences and Management, 4 (3), 166-168
Sharma, K, & Saptarshi D, (2017) Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction - With Special focus on the Online Cab Industry in India. International Journal of Business and Management, 12.192.10.5539/ijbm.v12n7p192 Accessed from:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317510767_Service_Quality_and_C... _Satisfaction_-_With_Special_focus_on_the_Online_Cab_Industry_in_India
Techarattanased, N, (2015) Service Quality and Consumer Behaviour on Metered Taxi Services . International Journal of Economics and Management Engineering , 9 (12)
Tessera, F A, Hussain, I A, & Ahmad, N, (2016). Service Quality and Hotel’s Customer Satisfaction: An Empirical Evidence from Ethiopia. Electronic Journal of Business and Management, 1(1), 24-32
Accessed from:
http://www.apu.edu.my/ejournals/ejbm/journal/2016/Paper3_Service_quality... l_customers_satisfaction.pdf
Zeithami, L, Berry L, & Parasuraman, A, (1990) Delivering Quality Service: Balancing Customers Perceptions and Expectations. New York: Free press